Metal Injection Molding vs Die Casting
Introduction
Metal injection molding vs Die casting is the major decision in metalworking process. Both these technologies are applied throughout industries in worldwide. Metal injection molding is an intricate process with several steps, it is suitable for small size parts with complex geometries. Otherwise, Die casting has less manufacturing steps, it is economical for simple parts with high -volume quantity.
What is Metal Injection Molding?
Metal injection molding (MIM) is a metalworking process, it applies powdered metal particles with binder materials to create net-shape metal parts and components. Furthermore, different from other technologies, MIM is able to produce small and complex parts at a lower cost. It is the only suitable technology for thin wall specifications as thin as 0.1 mm. In addition, its unique injection molding process can consolidate multiple parts in one single.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Process
Once comparing metal injection molding vs die casting process, we will notice that the MIM process is intensive and complex. Moreover, the normal MIM process including:
- Fine metal alloy powders are mixed with binder materials to form feedstock. Normally, we purchase feedstock for common MIM case. For specific case with unique MIM parts properties, we also can produce customized MIM feedstock.
- Inject feedstock into molds and get molded parts required structure. We call these molded parts as green parts.
- Remove binder materials by catalytic, solvent or thermal de-binding methods. We call debinded parts as brown parts. Otherwise, there are remaining binder materials left to contain brown parts structure.
- Sinter brown parts to create net-shape parts. This is the most critical step in metal injection molding. It determines the final properties of MIM parts.
- Apply post-operation like heat or surface treatment to achieve properties as requirement.
Metal injection molding has high design flexibility, this make it a desirable manufacturing technology in various industries.
MIM Parts Applications
The significant advantage of MIM parts is the small size with complex structure. In addition, MIM parts have excellent high-volume productivity with high quality. Therefore, this make MIM technology an efficient metalworking method. While other methods are difficult or impossible to manufacture.
ZCMIM has ability to produce complex MIM parts with tight tolerance. Such as our minimal accuracy can reach to 0.01 mm.
Metal part applications determine the final manufacturing method, whether metal injection molding or die casting. Metal injection molding is popular in many industries in reason of its unique value of cost-effective production.
- Automotive: system controller, electrical connecting parts.
- Medical: surgical instrument, sewing unit, B-ultrasonic instrument.
- Electronic: smart-wear, watch, headset, mobile-phone, cable & cord.
- Industrial: micro gear, machinery component, pepper spray part, drone part.
What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a metal casting technology for non-ferrous metal parts production. Metal materials are heated to molten, then injected into die molds in high pressure, finally cooled down and ejected out. The most common cast metal including: aluminium, cooper, lead and magnesium. Furthermore, depends on cast metal types, we can apply hot-chamber or cold-chamber casting machine.
There are four different die types for final cast parts impression.
- Single cavity: one part or component production.
- Multiple cavity: numbers of identical parts or component production.
- Unit die: different parts production in one cast cycle.
- Combination die: several assemble parts production.
Die Casting Process
The normal Die casting process including:
- Clamping: clean and clamp dies, then lubricate to prevent sticking.
- Injection: inject molten metal into dies with high pressure range form 140 MPa to 215 MPa. Injection time depends on parts complexity and wall thickness, multiple pattern or internal caverns take long time to fill.
- Cooling: Molten metal start cooling once enter the dies. While, we normally notice this cooling process after die cavity is filled. Parts geometric complexity and wall thickness determine long cooling times.
- Ejection: once metal parts is cooled down, the die halves is open and then eject molded metal parts out. After ejection, a new cast process start.
In addition, excess metal and flash should be trimmed by manual or other methods. Depends on final application, metal types and part size, there are different die casting methods for manufacturers. The three primary methods are gravity die casting, hot chamber die casting, cold chamber die casting.
Gravity Die Casting
This method is similar to its name, molten metal is poured into dies from the top area and filled by gravity force. In reason of metal inject into cavities by gravity, its injection speed is slower than pressurized die casting of hot or cold chamber. Therefore, there is less folding turbulence in gravity, and less trapped air in cast part. However, this slower process is not suitable for longer production.
Otherwise, pressurized die casting is applied for fast production with automation. It can produce cast parts with even metal distribution and thinner walls.
Cold Chamber Die Casting
Cold chamber die casting is suitable for metal with high melting points, for example aluminum, brass, and copper. We heat and molten metal materials in external furnace, then ladle into machine chamber, finally inject into dies under high pressure.
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Hot chamber die casting is perfect for metal with low melting points, such as tin, zinc, lead and magnesium alloys. All these metal materials are heated and melted in a furnace attached to the machine, then fed into dies directly through goosenecks.
Die Casting Applications
Die casting has versatile material options and design flexibility. Therefore, it is also another popular manufacturing method in different industries.
- Automotive: gear housings, transmission, retainers and engine components
- Medical: peristaltic pumps, hospital equipment controls, surgical devices, analysis machines.
- Industrial: hydrostatic axles, steel liner inserts, outboard gear case.
Parameter Comparison
Metal injection molding process is an effective way to produce high strength and tolerance MIM parts with complex geometries, which forms metal powder to parts shape and sinter it into final parts. MIM parts have excellent physical characteristics as high strength, wear and corrosion resistance, all these properties are difficult to achieve by other manufacturing processes.
Die casting process consist same injecting liquid metal into a die or mold, which is similar to MIM. Furthermore, Die casting has several economic advantages in right circumstance and component volume. It will save large cost for components designers, we can find normal parameters in these two technologies as following table:
| Parameters | Metal Injection Molding(MIM) | Die casting |
| Density | 98% | 100% |
| Mechanical Strength | High | High |
| Surface Finish | High | Medium |
| Miniaturization | High | Low |
| Geometric Complexity | High | Medium |
| Design Flexibility | High | Medium |
| Thin Wall Capability | High | Medium |
| Material Ranges | High | Medium |
| Product-ability | High | Medium |
| Post-operation Feasibility | Good | Good |
| Dimensional Tolerance | High | Medium |
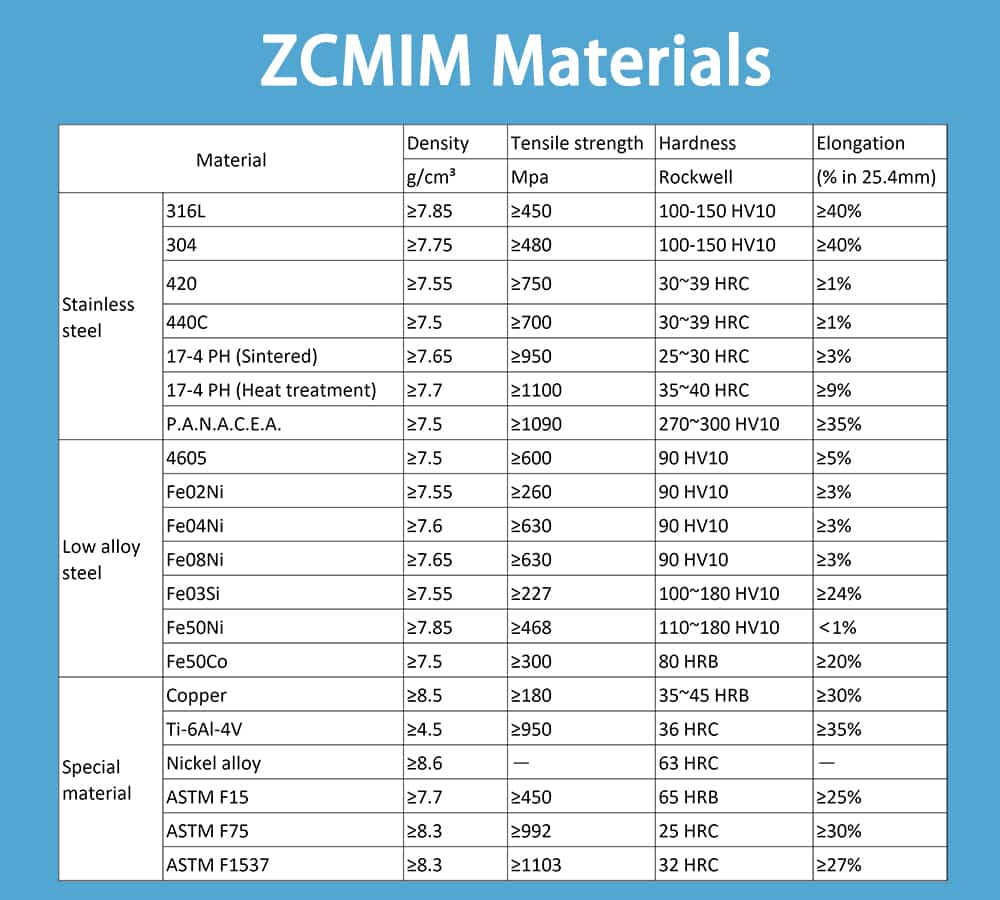
MIM vs Die Casting Materials
Major difference between Metal Injection Molding and Die Casting is material selection, metal injection molding uses steel or other MIM alloys, the common alloys including: stainless steels, titanium, nickel, tungsten, copper and various combinations. However, Die casting often use non-ferrous metal as aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy or zinc alloy.
It is easy to find out the main difference between MIM and Die casting material is metal melting point. Normally, MIM can manufacture metal materials with higher melting point than Die casting. We summarize our common MIM materials in ZCMIM as the following:
MIM vs Die Casting Process Comparison
Die casting is a fast and economical way for high volume metal parts with simple shape. The metal material with low melting temperature like zinc, aluminum, copper and magnesium will be mixed into ingot. Then, ingot will be melted by die casting machines and central furnace. All molted alloys inject into dies or molds with pressure by pump. At last, cooling and ejection of final molded metal are the final steps of die casting. Its cycle time depends on component size, range from 1 to 30 seconds.
MIM is a dense and complex process, metal alloys are formed into very fine powder, and then mixed with thermoplastic binder into feedstock. The feedstock will be heated into liquid form and injected into molds, cooled and ejected from the mold as green parts. Then de-binding process use catalyst to remove most binder. Finally, sintering process will sinter fine metal powder to combination together, create strong net-shape metal component.
High Tolerance
Both MIM and Die casting are suitable for high-volume metal parts production. However, MIM still has higher tolerance than die casting, this guarantee that MIM can produce high repeatable metal parts. Metal Injection Molding focus on quality and accuracy, while Die casting has variable dimensions as trimming to remove excess materials.
Complex Geometries
MIM is more suitable for small metal parts manufacture with complex geometries. From above table, we can recognize small features less than 2 mm only can use MIM technology to process. Otherwise, die casting will never satisfy this requirement.
Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is the most critical factor for complex, specific and hollow metal parts. Die casting has little or no control of wall thickness and porosity, so it is unable to applied for products with thin walls. However, Metal Injection Molding works well in these case, as there are strict manufacturing parameters to follow.
Size & Weight
Die casting has wider manufacturing size than MIM. For production of metal parts under 200 grams, MIM has higher productivity than die casting. Furthermore, it is difficult to create thin section less than 0.5 mm in die casting, but easily to complete in MIM.
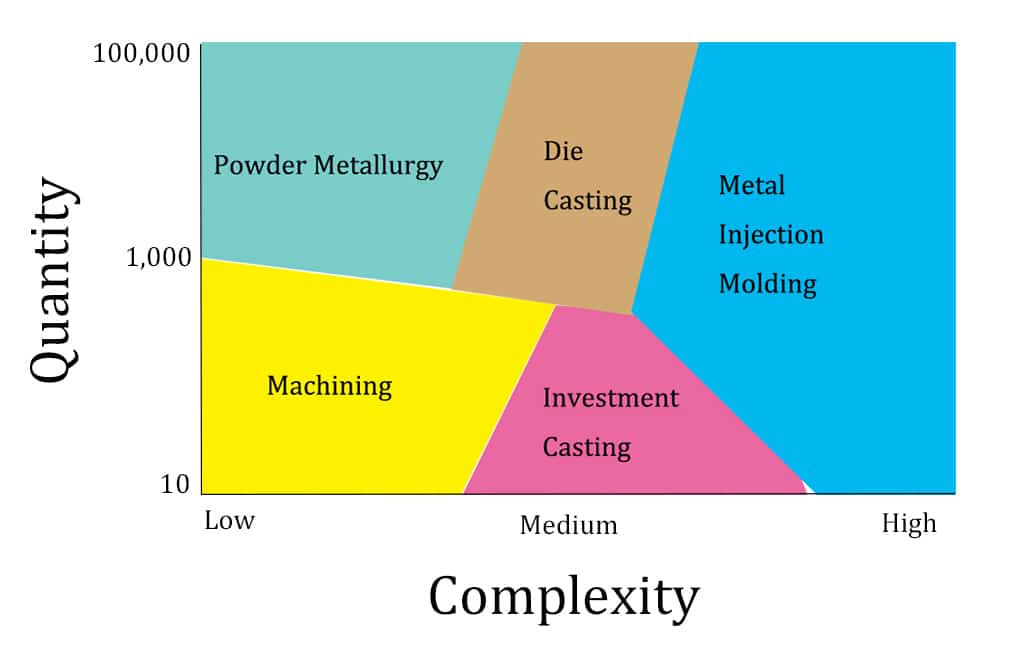
As these comparisons, we will notice that, MIM is ideal for small lightweight metal parts with complex geometries. The most suitable parts are smaller than 100 mm and less weight than 100 grams, in addition with production quantity above 10,000. All in all, MIM is the most cost-effective way for this item production, even comparing to die casting, precision machining.
Density
MIM technology mix metal powder with binder, then remove binder, sinter into MIM parts finally. So its normal density will achieve 95-99%, this is less than 100% of die casting. However, this never affect MIM parts functional properties, on the other hand, reduce MIM parts amount weight.
Mold Lifespan
Die casting mold is able to withstand high pressure and temperature, this will wear dies out quickly. However, dies also can use repeatedly up to 1 million, while Metal injection molding only can reach to 150K-300K shots in one mold.
Product Shrinkage
Metal Injection molding requires professional accounting for accurate shrinkage, as its shrinkage rate up to 30% in debinding and sintering process. However, Die Casting only has shrinkage rate of 0.001 per mm, this is not a major issue in metalworking process. In addition, isotropic shrinkage in die casting eliminates further challenges and cost in tooling.
Physical Properties
As MIM and die casting will both produce metal parts with conventional metal properties. In reason of various raw material usage in these two different method, we will find that MIM parts have more excellent chemical and physical properties:
High Strength
MIM parts always apply steel alloys, nickel alloys or titanium alloys, which have high mechanical properties than die casting materials like aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy or zinc alloy. Therefore, MIM parts strength is significant higher than die casting, including: surface hardness, wear performance, fatigue strength, fracture toughness, corrosion resistance.
Good Hardness
As MIM materials are normal metal with excellent surface hardness, it will encourage MIM parts perform better hardness than die casting. In addition, secondary operation as surface carburization will be used widely to increase MIM parts hardness.
Corrosion Resistance
MIM parts have higher surface roughness of 1 μm than die casting parts of 10 μm, this means MIM parts will perform better in corrosion resistance. As secondary operation of surface treatment will raise it into a new level.
Creep Resistance
Raw materials of MIM with excellent creep resistance decide high performance of MIM parts. However, Die casting materials as aluminum, zinc and magnesium alloys, are lack of these properties in nature, this will also affect performance of Die casting parts.
Metal Injection Molding vs Die Casting Advantages
Metal Injection Molding Advantages
- Net-shape metal parts production without secondary operations.
- Wide range of metal alloys, the most popular with stainless steel, copper, nickel.
- High mechanical strength after sintering.
- Tight tolerance reach to 0.01 mm.
- Various surface treatment.
- Full design freedom with complex geometries.
- Flexible production adjustment.
- No negative impact on tools in high-temperature alloys application.
- Virtual no material waste.
Metal Injection Molding Disadvantages
- Higher cost than die casting.
- Lower die lifespan (150K-300K shots).
- Accurate account for shrinkage up to 30% in sintering stage.
- High initial set-up cost.
Die Casting Advantages
- Up to 30% cost saving than MIM.
- Wide range of applications and industries.
- Long die life with 1 Million compared to 150-300K with MIM.
- Complex fasteners or inserts for final products.
- Fully automated process with labor cost saving.
Die Casting Disadvantages
- Common porosity challenge.
- Expensive dies to withstand high pressure and high temperature.
- Expensive and complex to set up.
- Unsuitable for small volume production.
MIM vs Die Casting Summary
Small Size Manufacturing
MIM is a considerable economic manufacturing technology for small complex parts. Because it applies fine metal powders for further metal parts production, larger size parts are not cost-effective. The most suitable part weight is between 0.1 and 200 grams. Furthermore, its design flexibility allows features complexity without additional cost, such as threads, miniaturization, identity text or graph. At last, metal injection molding technology can reach to the thinnest wall thickness of 0.1 mm.
Metal injection molding is more affordable for large volume production, it is cost-saving once production volume over 10,000.

High and Low Volume Manufacturing
Die casting is a better option for the large complex parts with low-volume production. There are affordable metal options with limited waste in die casting, no matter simple or complex parts. Therefore, die casting is affordable for both high and low volume production.
Conclusion
Although die casting seems more cost-effective than MIM, consider about all aspects of materials, process and properties. MIM has its unique characters to satisfy special metal parts requirement. Its wider range of materials choices and corresponding properties are key factors attract millions of customers in worldwide.
ZCMIM provides the best metal injection molding for customer in worldwide, our experienced engineers team and excellent facilities will satisfy your any projects’ requirement.